Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
This is a result of compression of the median nerve to the hand.
Anatomy
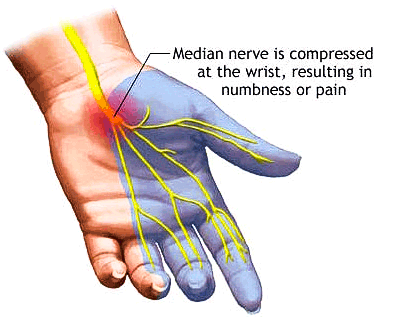
Median nerve is compressed at the wrist.
Symptoms
Patient typically complains of tingling or pain in all the fingers of the hand, with the exception of the little finger. There may be numbness and weakness in those fingers.
These symptoms tend to be very noticeable at night and may be alleviated by shaking of the hand.
These symptoms tend to be very noticeable at night and may be alleviated by shaking of the hand.
Causes
The median nerve runs into the hand through a small tunnel called the 'Carpal Tunnel'. The roof of this tunnel is called the Flexor Retinaculum or Transverse Carpal Ligament. This consists of a tough piece of tissue.
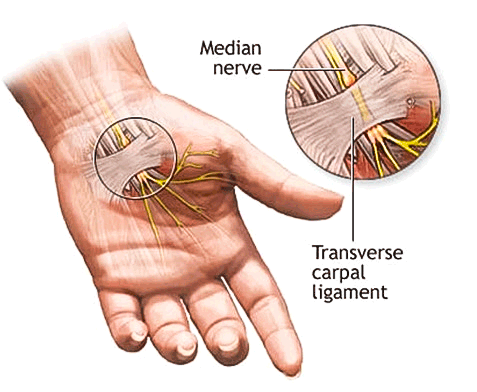
Median Nerve anatomy.
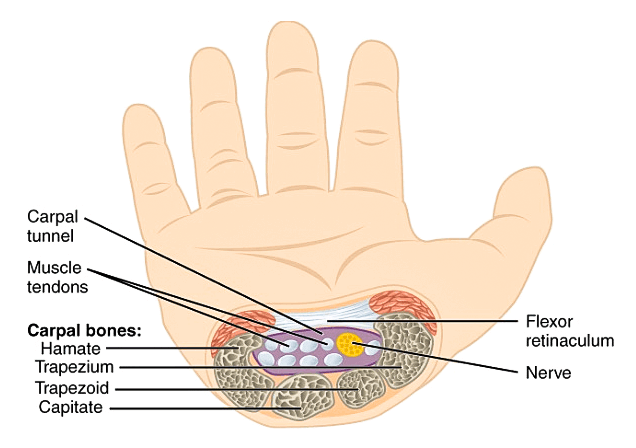
Carpel Tunnel.
Carpal tunnel syndrome results from compression of the median nerve in this tunnel. This may occur in the following situations:
- Diseases such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and hypothyroidism
- Repeated frequent hand/wrist motion.
- Work environment – working with vibrating tools may predispose to this complaint.
- Pregnancy
- Obesity
- Idiopathic – no obvious cause identified.
Diagnosis
This is done through the history of the complaint. A physical examination of the hand will also be performed.
Specific investigations that may be undertaken include:
Specific investigations that may be undertaken include:
- Nerve conduction test
- Ultrasound of the wrist area.
Management
Management options are:
1. Correction of the underlying cause of the carpal tunnel syndrome.
2. Pain relief and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAID)
1. Correction of the underlying cause of the carpal tunnel syndrome.
2. Pain relief and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAID)
- these provide pain relief from the condition
- however, there is no scientific evidence that these medications improve the syndrome.
- may provide relieve to night time symptoms
- may also temporise the condition during pregnancy.
Surgery
This is a minor surgery that can be performed under local (with or without sedation) or general anaesthetic. A small incision (cut on the skin) is made in the middle of the wrist. The flexor retinaculum is divided and the median nerve is freed from the compression.
The skin is then sutured closed.
The skin is then sutured closed.
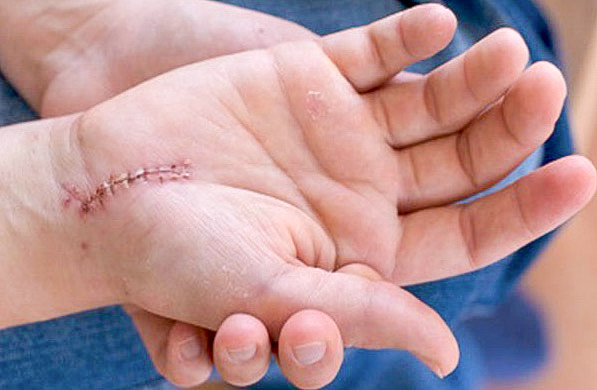
Carpal Tunnel scar.
Complications
- Incomplete release of the nerve
- Nerve or tendon injuries
- Scar tissue formation
- Wound infection.
Postoperative management
- Patient typically will have discomfort for 1–2 weeks.
- Working condition may need to be modified accordingly in this period.
- Hand exercise after the surgery is strongly encouraged.
Clinical Associate Professor Hairul Ahmad MBBS FRACS
Upper Gastrointestinal, Advanced Laparoscopic and General Surgery
Perth, Western Australia
Perth, Western Australia
Practice Details
Suite 12, Waikiki Specialist Centre,
221 Willmott Drive, Waikiki WA 6169
Please call (08) 9592 2298 for an appointment.
Fax: (08) 6314 1524
or email us
Office hours
9am–4pm Monday to Friday
Affiliations




© 2022 Perth General Surgery.
All Rights Reserved. Content and images on this website are subject to copyright.